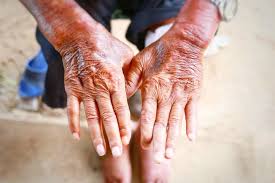
Scleroderma
Scleroderma
- Scleroderma is a rare autoimmune connective tissue disease.
- It causes the body to produce too much collagen, leading to hardening and tightening of the skin.
- In some cases, it also affects internal organs such as the lungs, kidneys, heart, and digestive system.
- There are two main types:
- Localized scleroderma – affects only the skin.
- Systemic sclerosis – affects both skin and internal organs.
- Common symptoms include thick, shiny skin, Raynaud’s phenomenon (fingers turning white/blue in cold), joint stiffness, heartburn, and breathing difficulties.
- The exact cause is unknown but involves an abnormal immune response plus genetic and environmental factors.
- More common in women aged 30–50 years.
- No cure exists, but early treatment with medicines, physiotherapy, and lifestyle measures helps control symptoms and prevent complications.
What are signs and symptoms of Scleroderma?
Here are the common signs and symptoms of Scleroderma
- Skin changes
- Hard, thickened, shiny, or tight skin (often starting in fingers, hands, or face)
- Swelling and stiffness of fingers (sclerodactyly)
- Skin patches that appear lighter or darker than normal
- Raynaud’s phenomenon
- Fingers or toes turn white, blue, or red in response to cold or stress
- Tingling, numbness, or pain in affected areas
- Joint and muscle problems
- Joint stiffness, swelling, or pain
- Muscle weakness or aching
- Digestive system issues
- Heartburn, acid reflux, or difficulty swallowing
- Bloating, constipation, diarrhea, or poor absorption of nutrients
- Lung involvement
- Shortness of breath
- Dry cough
- Risk of pulmonary fibrosis (scarring) or pulmonary hypertension
- Kidney problems
- High blood pressure
- Rare but serious condition: scleroderma renal crisis
- Heart symptoms
- Irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia)
- Chest pain or heart failure in advanced cases
What are common causes of Scleroderma?
- Immune system dysfunction – The immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s tissues, leading to excess collagen production.
- Excess collagen buildup – Overproduction and accumulation of collagen causes skin thickening and organ fibrosis.
- Genetic predisposition – Family history of autoimmune diseases increases risk.
- Environmental triggers – Exposure to certain chemicals (silica dust, solvents, pesticides) may trigger the disease in susceptible individuals.
- Vascular problems – Abnormal narrowing and damage of small blood vessels contribute to tissue injury.
- Gender and age – More common in women between 30–50 years.
- Autoimmune association – Often linked with other autoimmune conditions such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, or Sjögren’s syndrome.
Fast Facts on Scleroderma?
- Scleroderma means “hard skin” – caused by excess collagen in the body.
- It is a rare autoimmune disease that can affect the skin, joints, and internal organs.
- Women are 3–4 times more likely to develop scleroderma than men.
- Most cases are diagnosed between the ages of 30 and 50 years.
- Two main types: Localized scleroderma (skin only) and Systemic sclerosis (skin + organs).
- Raynaud’s phenomenon (fingers/toes turning white or blue in cold) is often the first sign.
- No cure exists, but early treatment helps control symptoms and prevent complications.
- With proper care, many patients can lead active, productive lives.
How Scleroderma is Diagnosed ?
- Medical history & physical exam – Doctor checks symptoms like skin thickening, Raynaud’s phenomenon, joint stiffness, or digestive problems.
- Blood tests – To detect specific autoantibodies such as ANA (antinuclear antibody), anti-centromere, or anti-Scl-70, which are commonly seen in scleroderma.
- Skin biopsy – A small sample of skin may be examined under a microscope to confirm excess collagen buildup.
- Imaging tests – Chest X-rays, CT scans, or echocardiography may be used to check lungs and heart involvement.
- Pulmonary function tests – To measure how well the lungs are working if breathing issues are suspected.
- Nailfold capillaroscopy – A special test to look at tiny blood vessels near fingernails, often abnormal in scleroderma.
How Scleroderma is Treated ?
- No permanent cure exists, but treatments help manage symptoms, prevent complications, and improve quality of life.
- Medications
- Immunosuppressants (to reduce immune system overactivity)
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (for joint and muscle pain)
- Vasodilators & calcium channel blockers (to improve blood flow in Raynaud’s phenomenon)
- Proton pump inhibitors (for acid reflux/heartburn)
- Physical therapy & exercise – Keeps joints flexible, improves circulation, and reduces stiffness.
- Skin & lung care – Moisturizers for skin; specific treatments for lung fibrosis or pulmonary hypertension if present.
- Lifestyle changes – Avoid smoking, protect hands/feet from cold, eat a balanced diet, and manage stress.
- Regular monitoring – Early detection of organ involvement (lungs, heart, kidneys) through periodic tests is crucial.
What happens if left untreated ?
If scleroderma is left untreated, the disease can progress and cause serious complications beyond skin changes. Over time, excessive collagen buildup may lead to permanent skin tightening, joint stiffness, and reduced mobility. Internal organs such as the lungs, kidneys, heart, and digestive system can also be affected, resulting in pulmonary fibrosis, high blood pressure, heart problems, or severe digestive issues. Additionally, untreated scleroderma increases the risk of organ failure and significantly impacts quality of life. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to control symptoms, prevent organ damage, and maintain daily functioning.
How OARC Can Help?
At OARC, we offer holistic care to patients suffering from all kind of arthritis and autoimmune diseases by our renowned rheumatologist. Because of chronic illness of the disease, we spend some time with the patient helping them to know about their disease, and demystify the myths regarding the disease and treatment. We have collaboration with NABL accredited laboAStory where all kind of blood tests can be done at reasonable costs. We also have patient support system where patient can approach in case of any emergency. We believe in a friendly relation with patients so that they can share all their sufferings and get the best possible treatment.